Blog
Solutions in Metal Fastening: The Advantages of Stud Welding
Stud Welding: Revolutionizing Productivity and Reliability in Metal Fastening
Manufacturing companies today face the dilemma of increasing productivity while maintaining high product quality. In the area of metal fastening, stud welding is a process that answers both sides of this dilemma.
This guide was developed to present the stud welding process, its advantages, and its wide-ranging applications, as well as to provide comparisons with other metal fastening processes.
Compared with many other welding and fastening processes such as drilling and tapping, resistance required, the process yields significant productivity improvements and cost savings. At the same time, stud welding provides a high quality, single-sided fastening process that is secure and resists breaking or loosening.
Understanding Stud Welding: Process, Techniques, and Benefits
Stud welding is a process by which a metal stud is joined to a metal workpiece by heating both parts with an arc. A key factor that differentiates stud welding from other fastening processes is that the fastener is attached to the workpiece without marring the other side.
This guide will discuss Arc stud welding and CD (capacitor discharge) stud welding methods.
Arc Stud Welding: Techniques, Applications, and Benefits
The Arc stud welding method provides highly reliable fastening for a wide variety of applications. This method allows almost any size or configuration of metal stud to be welded quickly to a workpiece, while providing maximum weld penetration and reliability.
Arc stud welding permits strong, one-sided welds on base metals with thicknesses starting at 0.048" (1.2 mm). It produces welds in as little as 0.06 seconds.
Arc stud welding utilizes a dc power supply to create the arc; a stud welding gun; metal fasteners; and in some cases, ferrules. There are three common techniques of Arc stud welding: Drawn Arc stud welding, Short Arc stud welding, and Gas Arc stud welding.
Drawn Arc Stud Welding
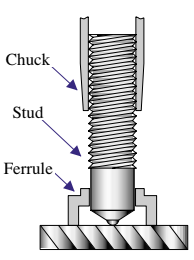
In the Drawn Arc technique, the stud is loaded into the stud gun chuck, and a ferrule (a disposable ceramic shield that contains the molten pool of metal) is placed over the end. The gun is placed against the work position. When the trigger is pressed, the dc power supply sends a signal that energizes the gun’s internal lift mechanism lifting the stud, drawing the pilot arc. The pilot arc establishes a path for the weld current which initiates after the pilot arc. Upon completion of the proper arcing time, which is proportional to the square area of the surface being melted, the lift mechanism is de-energized. This causes the stud to plunge into the molten pool of metal. A plunge dampener is often used on larger studs to decelerate the stud’s movement onto the molten pool, minimizing splash. As the stud and the base metal join, the metal begins to solidify and the weld is created. The gun is lifted, and the ferrule is discarded.
The Drawn Arc technique uses flux embedded in the stud to cleanse the atmosphere during the weld. During arcing, the flux is vaporized and combines with the contaminating elements in the atmosphere to keep the weld zone clean.
Step-by-Step Execution of Drawn Arc Stud Welding
- The stud is loaded into the chuck and the ferrule is loaded into the ferrule grip.

- The gun is positioned and the main gun spring is compressed.
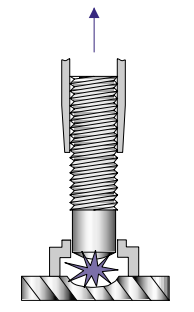
- The trigger is pressed and the stud lifts off the workpiece. An arc is created by a dc power supply, melting the full diameter of the stud and the same area of the base material.
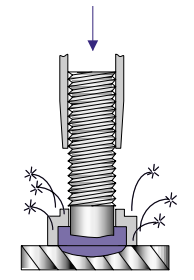
- After the arcing time is completed, the main spring plunges the stud into the molten pool of metal.
- The gun is withdrawn from the welded stud. The ferrule is broken away and discarded.

Short Arc Stud Welding
The Short Arc technique is much like Drawn Arc, yet it uses no flux load or ferrule, and it offers the shortest welding times of the Arc stud welding techniques. It is characterized by high currents and short weld times. While it may be suitable for many high volume applications, it can produce porous welds and should therefore be selected when speed and cost are a priority over weld strength.
The short weld times minimize the effects of porosity while the high current maintains the needed energy.
Gas Arc Stud Welding
The Gas Arc technique uses inert shielding gas with no flux or ferrule, making it easier to automate, but it provides less fillet control and less depth of penetration in comparison with the Drawn Arc technique. In Gas Arc welding, a spark shield, which delivers gas, replaces the ferrule. The stud is loaded and the gun is positioned for welding. When the user pulls the trigger, shielding gas (“gas pre-flow”) floods the welding zone. The stud is lifted, and an arc is generated. While the stud remains lifted, the weld current melts the stud and base metal. When the arc time is complete, the gun is plunged into the molten pool. A post-flow of gas is introduced to the weld, flowing until the molten metal cools. The gun can then be removed. Since no ferrule is used, this process lends itself well to automation and robotics.
The Advantages of Arc Stud Welding: Quality, Productivity, Economics
Arc stud welding provides excellent welding success under a broad range of conditions. It produces a full cross-sectional weld, forming a bond that is stronger than the surrounding metal. This section examines its quality, productivity, and cost advantages.
Elevating Weld Quality with Arc Stud Welding
Improved Weld Strength
Arc stud welding produces a strong, one-sided weld. The welds are vibration-proof and resistant to breaking, loosening, or weakening.
Enhanced Aesthetic Appeal
In applications where quality is measured in part by attractive appearance, Arc stud welding offers excellent cosmetic appeal because the reverse side is not marred.
Design Freedom in Arc Stud Welding
Arc stud welding’s one-sided fastening process permits greater design versatility.
Boosting Productivity with Arc Stud Welding
Streamlined Manufacturing with Faster Arc Stud Techniques
Compared with other typical fastening processes, Arc stud welding permits faster, easier manufacturing because each weld is achieved in less than a second, and because welds can be achieved with access to only one side.
Simplified Manufacturing Processes
Arc stud welding eliminates punching, drilling, tapping, and riveting. With special techniques, it permits welding on painted surfaces, eliminating the need for pre-grinding and recoating.
Economic Advantages of Arc Stud Welding: A Cost-Benefit Analysis
Significant Labor Savings
Labor costs are dramatically reduced with Arc stud welding because through-hole preparation is eliminated and the process can be completed by a single worker.
Reduced Fabrication Costs
Often, an expensive, odd-shaped piece can be duplicated inexpensively by welding several studs to a simple stock shape to form a metal fabrication.
Arc Stud Welding vs Traditional Techniques: Drilling/Tapping and Conventional Bolting
- Arc Stud Welding utilizes one-sided fastening for better appearance and design freedom
- No drilling and tapping in arc stud welding projects
- Only one-person operation
- Arc stud welding won’t vibrate loose
- High-speed automatic equipment can be used when arc stud welding
- Reverse sides may be finished before welding
- Nuts or gaskets to prevent leaking aren’t required in arc stud welding
Capacitor Discharge (CD) Stud Welding: Techniques, Applications, and Benefits
Capacitor Discharge (CD) stud welding, using very short weld times, permits the welding of small-diameter studs to thin, lightweight materials. The weld cycle can be completed in 0.01 seconds on material as thin as 0.020" (0.5mm). These fast weld times minimize heat buildup, resulting in welds with very little distortion, discoloration, or burning. Therefore, CD stud welding is often used when appearance is a critical product feature. CD stud welding uses a capacitor storage system to produce a rapid electrical discharge, stud welding guns, and fasteners. No ferrules or flux are needed. The CD stud welding method, used mainly for welding mild steel, stainless steel, and aluminum studs, includes two primary techniques: Contact and Gap. Both require a specially designed stud with a projection, or ignition tip, on its weld end. This tip provides accurate welding time control with precise repeatability.
Contact CD Stud Welding
During Contact CD stud welding, the stud is loaded into the gun and positioned in contact with the workpiece. Energy is then instantaneously discharged from capacitors through the stud’s projection. Since the size of the ignition tip cannot handle the current density of the capacitor’s stored energy, it vaporizes, creating a gap that allows an arc to be formed. As the arc begins to melt the stud and workpiece, the two pieces are forced together, and a weld is produced as the metal cools.
Gap CD Stud Welding

Gap CD stud welding offers shorter weld times with higher current densities when compared with contact CD stud welding. With such quick welding capability, this technique is particularly well suited to cosmetic applications, since it produces very minimal backside marking.
In Gap CD stud welding, the stud is positioned above, not against, the workpiece. When the stud is released, it accelerates toward the workpiece. Simultaneously, an open-circuit voltage is applied to the gap. As in Contact CD stud welding, the ignition tip is vaporized and the pieces are melted and forced together to form the weld. Because the stud starts in motion during this welding technique, the weld times are even faster than those produced in Contact stud welding—approximately 0.004 seconds with peak currents of 9,000 amps.
Gap CD stud welding is ideal when welding aluminum or non-ferrous alloys, which have an excellent ability to conduct heat. With slower techniques, the base material can draw heat away too fast for a weld to occur; but Gap CD welding’s fast weld times overcome this phenomenon.
Step-by-Step Execution of Gap and Contact CD Stud Welding
In Gap CD stud welding, the gun is positioned over the target at the start of the process, then begins to move toward the workpiece.

In both Gap and Contact CD stud welding, the stud makes contact with the workpiece. The main difference between the processes is that the Contact CD process begins in this position.

Upon contact with the base metal, the ignition tip vaporizes and an arc is formed. This arc melts the full diameter of the stud and the same area of the base metal.

As the pieces are forced together by spring pressure, weight, gravity, or air pressure, the stud forms a complete bond with the base material.

CD Stud Welding Advantages

CD stud welding creates high integrity welds even on thin gauge materials. Additionally, it allows the welding of dissimilar metals because the weld penetration is so slight that metallurgical problems are prevented. The quality, productivity, and cost advantages of CD stud welding include:
Achieving Superior Quality with CD Stud Welding
Minimizing Burn Marks from CD Stud Welding
Often important in cosmetic applications, CD stud welding offers appealing one-sided welds with no reverse side dimples.
Improving Strength in Lightweight Applications from CD Stud Welding
On very lightweight material that would be compromised when using other fastening processes, CD stud welding creates a strong, high quality bond.
Reducing Backside Marking from CD Stud Welding
CD stud welding allows backsides to be prepainted without damage to the paint.
Streamlining Productivity with CD Stud Welding
Enhanced Process Speed from CD Stud Welding
With its extremely short weld times, CD stud welding substantially increases productivity.
Reduce Assembly Steps by Using CD Stud Welding
Like Arc stud welding, CD stud welding eliminates punching, drilling, tapping, and riveting.
Economic Efficiency of CD Stud Welding
Reduce Labor Costs with CD Stud Welding
As in Arc stud welding, the CD stud welding process saves significant costs by eliminating through-hole preparation.
Lower Fabrication Costs with CD Stud Welding
Often, an expensive, odd-shaped piece can be duplicated inexpensively by welding several studs to a simple stock shape to form a metal fabrication.
Comparing CD Stud Welding with Clinch Fastening: A Tactical Overview
- No lengthy setup in CD stud welding
- Can use portable CD stud welding equipment
- CD stud welding enables one-sided fastening
- CD stud welding leads to secure, durable holds
- CD stud welding allows the finish of reverse side prior to welding
- CD stud welds won’t vibrate loose
Wide-Ranging Applications of Stud Welding
As discussed earlier, Arc stud welding meets a broad variety of metal fabrication requirements, while CD stud welding is well suited for the welding of studs to lightweight or thin gauge materials.
Stud welding may be integrated with an automated process using an automatic feed system, to yield weld rates of up to 45 studs per minute depending on size and process.
Arc Stud Welding Applications Across Industries
Because a weld produced by the Arc stud welding process offers such benefits as high structural integrity, excellent productivity, leak resistance, corrosion resistance, minimized noise and vibration, and many other benefits, it has found extensive use in a wide range of applications, including:
Automotive Industry Applications of Arc Stud Welding
- Heat shields
- Power steering and dashboard components
- Instrument panels
- Insulation
- Exhaust systems
- Lighting systems
- Hydraulic/brake/fluid lines
- Electrical wire routing
- Trim
Construction Sector Uses from Arc Stud Welding
- Bridges
- Buildings
- Conduit
- Piping
Agricultural Arc Stud Welding Uses
- Fenders
- Brackets
- Cabs
- Spreaders
- Shrouding
- Thresher teeth
- Wiring and hose management
Highway and Interstate Arc Stud Welding Applications
- Cover plates
- Non-skid devices
- Wiring and hose management
Arc Stud Welding Used in an Institutional Apparatus
- Commercial dishwashers
- Bottle washers
- Cooking equipment
- Griddle plate assemblies
Furniture Design From Arc Stud Welding
- Metal household and office furniture
- Lawn furniture
- Shelving
- Racks
Metal Products Made Using Arc Stud Welding
- Barbecue equipment
- Enclosures
- Heating/plumbing apparatus
- Insulation enclosures
- HVAC units
- Water storage systems
Industrial Capabilities From Arc Stud Welding
- Inspection cover plate attachments
- Enclosures
- Flow indicators
- Material handling equipment
- Controls
Power Generation and Distribution Arc Stud Welding Applications
- Power transformer tanks
- Transducers
Shipbuilding Uses from Arc Stud Welding
- Insulation
- Wire management
- Hatch covers
Arc Stud Welding in Lawn and Garden Applications
- Tractors
- Mowers
- Seeders
Arc Stud Welding in Electronics and Electrical Devices
- Electrical enclosures
- Hydraulic lines
Various Applications of CD Stud Welding
Providing fast welds on lightweight material with minimal distortion, CD stud welding is widely used in the following areas:
Jewelry Making with CD Stud Welding
- Earrings
- Pins
CD Stud Welding for Hardware Manufacturing
- Brackets
- Cleats
- Tool handles
Cookware Production Using CD Stud Welding
- Utensils
- Pots and pans
- Handles
CD Welding in Electrical Houseware Production
- Electric frying pans
- Cookers
- Oven assemblies
- Microwave guides
Electrical Device and Electronic Fabrication Through CD Stud Welding
- Components
- Terminals
- Pumps
- Motors
- Communication equipment
- Electronic systems
Door Manufacturing with CD Stud Welding
- Commercial doors
- Escutcheon plates
- Insulation
Stud Welding Comparative Advantages to Other Welding Types
Stud Welding’s Advantages Compared to Brazing and Soldering
- Less training required for stud welding
- Faster process
- Less installed cost
- Ability to join after surface is painted
Stud Welding's Benefits Over Boring, Drilling, and Tapping
- Faster process
- No through-hole preparation
- Less installed cost
- No reverse side marking
- Resistance to leaks and vibration
Stud Welding Benefits in Comparison to Clinch Fastening and Resistance Welding
- No two-sided access required
- No visible head
- No high pressure required for installation
- No through-hole preparation
- Portable equipment
- No reverse side marking
- Resistance to leaks and vibration
Stud Welding's Advantages Over Conventional Bolting
- Faster process
- No two-sided access required
- No visible head
- Assembly without requiring two hands
- No through-hole preparation
- Less installed cost
- No reverse side marking
- Resistance to leaks and vibration
How Stud Welding is Superior to Hand Welding
- Less training
- Faster process
- Less installed cost
- Works equally well on thick or thin material
- No reverse side marking
- Ability to join after surface is painted
- Resistance to leaks and vibration
Making the Right Stud Welding Decision for Your Project
To determine whether stud welding is the optimum metal fastening method for your requirements, analyze your specifications, consider such factors as productivity, quality, aesthetics, and engineering assistance. If appearance is important, compare stud welding’s one-sided fastening process with two-sided processes. When comparing welding times between processes, be sure to compare the steps involved in one process versus another, in order to reach an accurate assessment of productivity rates.
If you have selected the stud welding process, consider the following qualifications when choosing a stud welding partner:
Designing and Engineering Your Product Through Stud Welding
Is the manufacturer an innovator, offering solutions for promoting efficiencies and solving problems in your process? Do they offer accessible on-staff technical support? How responsive are they?
Choosing the Right Stud Welding Equipment
Does the supplier manufacture Arc and CD stud welding equipment, guns, and studs meeting various size and power requirements? Do they offer a complete package including power supplies, stud welding guns, studs and accessories? Can they recommend the optimal equipment and/or complete package for your unique application? Do they assist you in determining the optimum equipment, fasteners, and accessories?
Ease in Using Stud Welding Equipment
Is the equipment easy to use? Does it offer advanced technology, such as digital features included on the equipment to help you increase your efficiency, flexibility, and reliability?
Value-Added Services from Stud Welding
Does the manufacturer provide additional process capabilities? Do they offer such value-added services as component reduction, secondary process elimination, waste minimization, and quality improvement to help you minimize costs and maximize your productivity?
Importance of Customer Support from Your Stud Welding Choice
Does the manufacturer provide training? Do they have maintenance programs in place, including routine maintenance and emergency/breakdown service? How quickly will they respond to your inquiries? Are they consistently available when you need them?
Evaluating the Experience of a Stud Welding Provider
How long has the manufacturer been in the stud welding industry? Do they offer the expertise to help you fulfill your unique metal fabrication requirements? Does the manufacturer have any active members in the American Welding Society?
Image Industries is a Leader in Reliable Stud Welding Solutions
Image Industries, Inc., founded in 1976, is a technology-driven leader in the design and manufacture of stud welding equipment and studs. Image was the first U.S. manufacturer to introduce digital stud welding equipment for quick, easy stud welding with greater productivity.
Image offers Arc and CD equipment along with fasteners in a variety of shapes, sizes, and gauges, including specialty fasteners. Our Smart WeldTM digital Arc stud welding equipment helps raise productivity with features like Auto WeldTM, which enables operators to determine weld parameters quickly by simply entering the fastener size and type of material.
Image provides imaginative, cost-effective solutions to fastening challenges. In addition to stud welding equipment and solutions, we offer cold forming capabilities which provide instant, repeatable forming of metal into predetermined shapes. Complete training, maintenance, and breakdown services are offered, with response to customer inquiries within 24 hours.
For more information on stud welding, or to discuss your metal fastening requirements with one of our experts, contact Image today.
Building lasting bonds since 1976.
Providing superior stud welding and stud welder parts and equipment isn't enough. We also strive to deliver better service and unmatched expertise. And that's exactly what we've been doing for more than 40 years.
Read About Our History